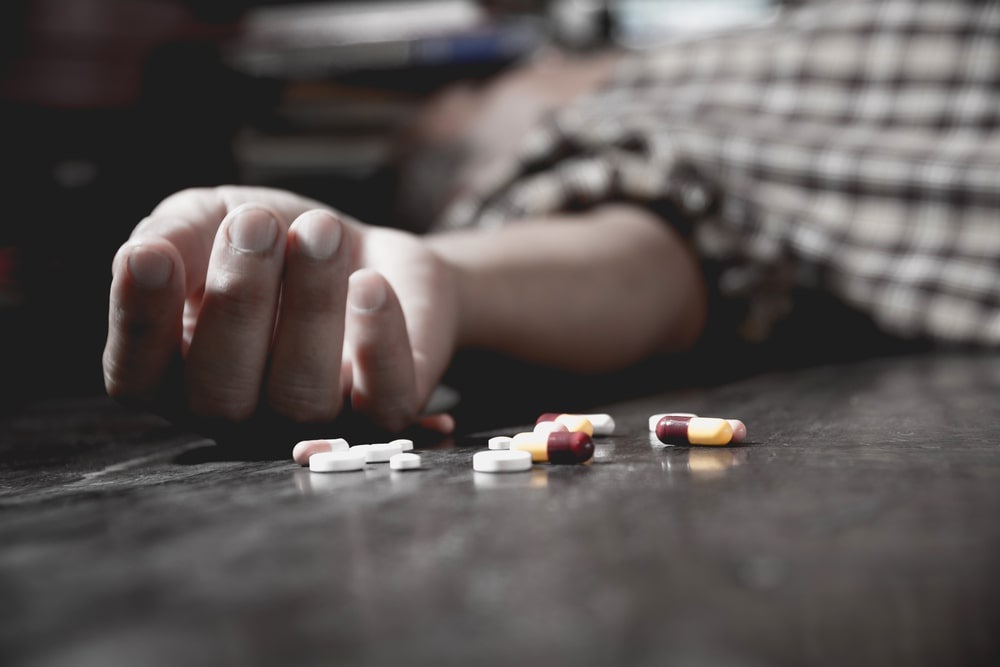
An overdose is the body’s reaction to ingesting an excessive amount of a chemical or combination of substances. Using illegal substances, booze, prescription medicines, etc., is possible. As overdoses are typically lethal, calling 911 is typically the best course of action. Even if someone has endured several overdoses, there is no guarantee that they will survive the upcoming one. Most addicts who pass away do so from respiratory failure. When they are unable to breathe, their heart, brain, and other organs are depleted of oxygen.
Overdose Symptoms and Signs
It’s crucial to be knowledgeable about the typical signs and symptoms of an overdose, whether you or someone you care about uses alcohol, drugs, or a mix of the two. The severity of an overdose drug will depend on the doses used, the substance consumed, the method of consumption, and the victim’s general health. Your physical signs might be, for instance:
- The (CNS) drugs that cause depression, coma, respiratory arrest, weak pulse, shallow breathing, and clammy skin.
- Hallucinogens: agitation, delirium, and psychotic symptoms.
- Inhalants: depression, coma, unconsciousness, arrhythmia, and untimely demise.
- Cannabis: extreme sleepiness, shaky gait, nausea, tachycardia, agitation, and psychosis.
- Opioids cause respiratory depression or arrest, clammy skin, cyanosis (bluish skin), low level of consciousness, and noticeably constricted pupils. Pupils can get dilated if anoxic brain injury has occurred.
- Stimulants: tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, agitation, arrhythmia, hallucinations, and other psychotic symptoms, seizures, and cardiovascular emergencies.
Your cognitive faculties may be impacted by an overdose as well. You might discover that you have trouble reading, having a hard time making sentences, and having short-term memory loss. You might see imaginary things, people, or animals during hallucinations. Agitation, paranoia, and violent, aggressive conduct might result from this. In severe circumstances, individuals will go through a life-threatening medical emergency, such as a heart attack, stroke, or total respiratory failure. They might also pass away or go into a coma.